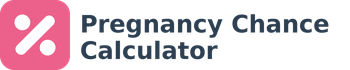Use this pregnancy due date calculator to work out your baby’s estimated due date (EDD), how many weeks pregnant you are, and which trimester you’re in. Enter the date of your last period, conception, intercourse, IVF transfer, or an early ultrasound.
Birth Probability Calendar
Birth Probability Calendar
Pregnancy Progress
Current Status
Key Dates
How to Use Our EDD Calculator
- Select your method: Choose how you want to calculate. "Last Period Date" is the most common, but you can also use Conception, Intercourse, IVF, or Ultrasound.
- Enter your details: Fill in the required fields for the method you’ve chosen. For example, for "Last Period Date," enter the first day of your last period and your usual cycle length.
- Calculate your due date: Click the "Calculate Due Date" button to see your estimated due date, how many weeks pregnant you are, and the birth window calendar.
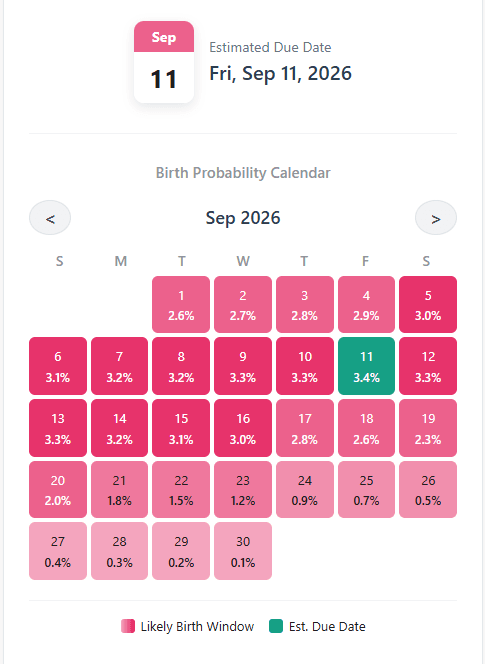
The Science: How Your Due Date is Calculated
This pregnancy due date calculator follows the same methods doctors use to estimate your Estimated Date of Delivery (EDD). While it looks like a single date, the calculation depends on the information you provide, such as your last menstrual period, cycle length, conception timing, IVF transfer or ultrasound findings.
- From Last Menstrual Period (LMP): This is the standard method. We add 280 days (40 weeks) to the first day of your last period. Crucially, we then adjust this date based on your average cycle length to create a more personalized and accurate timeline.
- From Conception or Intercourse: A full-term pregnancy lasts about 266 days (38 weeks) from the date of conception. If you provide a conception date, we add 266 days. If you provide an intercourse date, we first add ~2 days to estimate conception, then add 266 days.
- From an IVF Transfer: This method is highly precise. We calculate your due date based on the age of the embryo at transfer (either 3 or 5 days) and the date of the transfer.
- From an Ultrasound: An early ultrasound is the most accurate way to date a pregnancy. We use the gestational age provided by the scan and the date of the ultrasound to accurately pinpoint your due date.
Your Pregnancy Timeline: Key Milestones
Weeks 6-9: First Heartbeat
The baby's heartbeat can typically be detected for the first time via a transvaginal ultrasound. This is often one of the first and most exciting milestones for new parents.
Week 12: End of First Trimester
Reaching the end of the first trimester is a significant milestone. At this point, the risk of miscarriage drops substantially, and many people feel more comfortable sharing their news.
Weeks 18-22: Anatomy Scan & Gender Reveal
The mid-pregnancy ultrasound, or anatomy scan, checks on the baby's development. This is often when parents can, if they choose, find out the baby's sex.
Week 24: Viability
This is generally considered the point of viability, meaning a baby born at this stage has a chance of survival with intensive medical care. Every week from this point on significantly increases that chance.
Week 28: End of Second Trimester
As you enter the third trimester, your baby's development focuses on gaining weight and preparing for birth. You may begin to see your healthcare provider more frequently for check-ups.
Week 37: Full Term
Congratulations, your baby is now considered "full term"! While your due date may still be a few weeks away, the baby's lungs are mature and they are ready for life outside the womb.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why is my due date an "estimate"?
Only about 4-5% of babies are born on their exact due date. Your EDD is the center of your "due date window," but it's completely normal to give birth in the two weeks before or after. Our Birth Probability Calendar helps you visualize this.
How accurate is this due date calculator?
Due dates are always estimates. Only a small percentage of babies are born on the exact estimated due date. Most births happen within a few weeks either side of the EDD. This calculator uses standard obstetric rules (for example, 280 days from the first day of your last menstrual period, or about 266 days from conception) and adjusts for cycle length, so results should be similar to those used in clinic tools. An early first-trimester ultrasound is usually more accurate than period-based dating, and your care team may change your due date if a scan suggests a different gestational age.
Can this due date calculator work if my cycles are irregular?
If your cycles are irregular, any period-based due date (including this calculator) will be less precise. You can still enter your best estimate of your usual cycle length, but there will be a wider range of possible delivery dates. In this situation, doctors often rely more on an early ultrasound to set or confirm the due date.
What is a "full-term" pregnancy?
Pregnancy terms are defined by how many weeks you are at delivery. Here's a quick guide:
- Early Term: 37 weeks, 0 days to 38 weeks, 6 days.
- Full Term: 39 weeks, 0 days to 40 weeks, 6 days. (The optimal window)
- Late Term: 41 weeks, 0 days to 41 weeks, 6 days.
- Post-term: 42 weeks, 0 days and beyond.
Which calculation method is most accurate?
An early first-trimester ultrasound is the clinical gold standard for dating a pregnancy. If your doctor has given you a due date based on a scan, that is the most reliable date to use.
How does my cycle length affect my due date?
The standard 280-day calculation assumes you ovulate on day 14 of a 28-day cycle. If your cycle is longer, you likely ovulate later, which pushes your due date back. If your cycle is shorter, you likely ovulate earlier, which moves your due date up. Our calculator handles this adjustment automatically.
Pregnancy Terms at a Glance
| Term | Weeks | What It Means |
|---|---|---|
| Preterm | < 37 | May need extra medical support |
| Early | 37 – 39 | Healthy, but final development is underway |
| Full | 39 – 41 | Optimal window for delivery |
| Late | 41 – 42 | Monitoring or induction may be discussed |
| Post-term | > 42 | Labor might be induced to reduce risks |
Medical Disclaimer
This information is for educational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always confirm your timeline and any health concerns with a qualified healthcare provider.